A team of researchers from the Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed an organic active adaptation transistor (OAAT).
The human eye is able to conduct a type of on-the-fly adaptation—when moving from a dark theater, for example, the eye automatically undergoes changes to respond to a bright day outside—and it is not as simple as just changing the amount of light let through the lens by opening or constricting the pupil. Changes must also take place in the back of the eye where different types of ions are transported. In this new effort, the researchers sought to replicate this process by creating a photo adaptive transistor device—one that might one day be used to restore vision in those with eye damage.
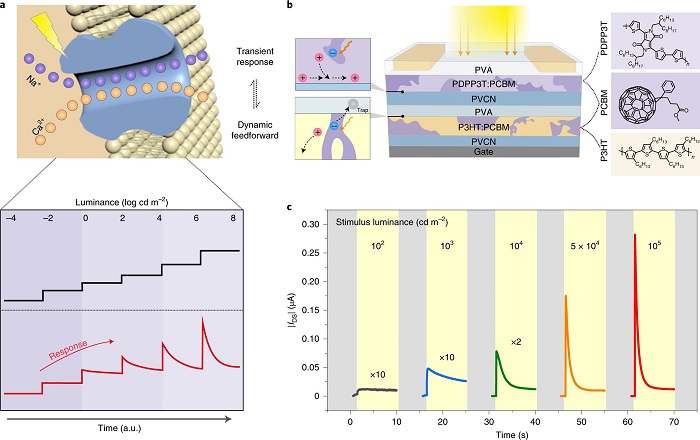
Shortly after embarking on their work, the researchers came upon a major hurdle—how to handle the conflicting demands of the charge transport—where both inhibition and photoexcitation are needed. After much experimentation, they came up with a novel idea—introducing two bulk heterojunctions as two different layers of their device. One would serve as a photo-responsive active layer, the other as a floating gate.
After more experimentation, the group came up with a fully functioning seven-layer device: The first layer was a polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), a dielectric. Underneath that sat the first heterojunction. Next came a poly(vinyl-cinnamate) (PCVN), another dielectric. Then, another layer of PVA, followed by the second heterojunction, then another PCVN layer, and finally a gate.
Once their device was complete the researchers discovered that they had no good way to test it. After three months of discussion, they came up with what they call the ‘active adaptation index’—it could be used to test adaptation in the human eye and then to compare that with their newly developed OAAT. They found the scores from the two sources to be remarkably similar.
The researchers suggest their work represents a first step toward creating adaptive devices for use both in robotics and in devices meant to replace organs in human patients.