The miniaturization of electronics has resulted in an ever-increasing global market for portable devices. Correspondingly, it has become necessary to develop smaller and more lightweight power sources to operate these devices. In particular, there has been a growing interest in implementing flexibility into the power sources themselves, which would be useful for potential applications in wearable and roll-up devices.
Fuel cells have a number of advantages over conventional batteries, such as having much higher energy density and reduced environmental impact. Until now, the manufacturing polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) that are small, light, and capable of mechanical movement has been challenging using conventional methods. PEMFCs are composed of end plates, bipolar plates, gaskets, membrane electrode assemblies (MEAs), and other assembly parts, of which the end plates and bipolar plates occupy 80 percent of the total weight. These plates are heavy, rigid, and inevitably cover a large volume, which increases the weight of the system. This means that simplifying and reshaping these components would greatly reduce the weight, in addition to paving the way towards the development of flexible PEMFCs.
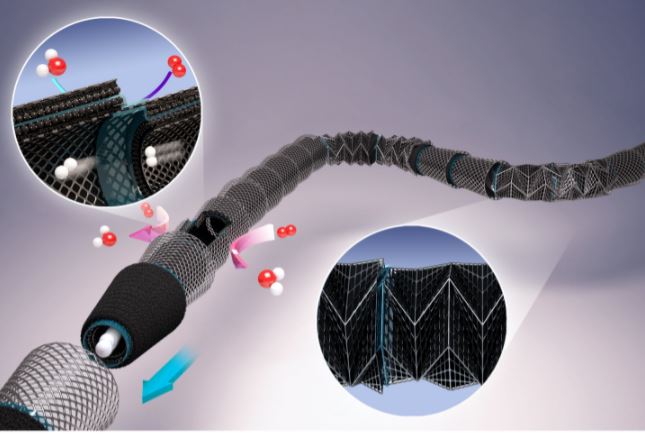
Led by professor SUNG Yung-Eun, researchers at the Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) in Seoul, South Korea reported the development of a lightweight and flexible passive air-breathing PEMFC. These new fuel cells, termed tubular PEMFC (t-PEMFC), are not only lightweight and of miniaturized form factor but are also flexible in design.
The basic unit of the t-PEMFC has a conical shape. The new conical design allowed for simplification of the components and to facilitate easier assembly by allowing the parts to be rolled up and stacked like paper cups. This greatly reduces the number of parts necessary for assembly, such as clamps and bolts, as well as removing the bulky end plates that are used in conventional fuel cells. As the inside of the tube itself can function as a channel, it also eliminates the need for a flow field plate. In addition, the bipolar plate is lightweight and compact due to being composed of stainless-steel mesh. As a result, the total weight of the parts excluding the membrane electrode assembly was reduced to less than 60 percent.
Another key feature of the new fuel cell is its flexible 3D structure based on the principle of origami. The conical reverse truss design allows the PEMFC to be easily folded and bent. The folding could reduce the volume by nearly 50 percent and 90 degrees bending is possible. It was confirmed that there was almost no degradation in performance after folding, and up to 90 percent of the initial performance was retained even when the cell was bent by 90 degrees.
Lastly, it is also possible to augment the total power output of these fuel cells by connecting multiple t-PEMFC modules in series. The individual units can be connected by simply inserting the tubular parts one after the other. The fuel cell in which two cells are connected in series was very compact with a volume of 0.565 cm3 and light with a weight of 0.22 g. A two-cell stack was able to achieve performances of 198 mW in power output and 897.7 W·kg-1specific power density when using humidified H2as a fuel source. The polarization curve measurement showed that the cells maintained the same performance even after more than 100 cycles. The stable operation of the cell was also possible using liquid methanol as fuel.
It is believed that the IBS team’s new innovative design will significantly advance the field of fuel cell development. It is expected that the flexible t-PEMFC can have a wide range of applications in devices that require mechanical movements, such as drones, robots, electrical wires, and small pipelines that require mobility. It is expected that this technology can also be applied in electrochemical devices based on polymer membrane electrodes, which are used in various processes including water electrolysis and CO2 conversion.