Despite our remarkable advances in medicine and healthcare, the cure to cancer continues to elude us. On the bright side, we have made considerable progress in detecting several cancers in earlier stages, allowing doctors to provide treatments that increase long-term survival. The credit for this is due to “integrated diagnosis,” an approach to patient care that combines molecular information and medical imaging data to diagnose the cancer type and, eventually, predict treatment outcomes.
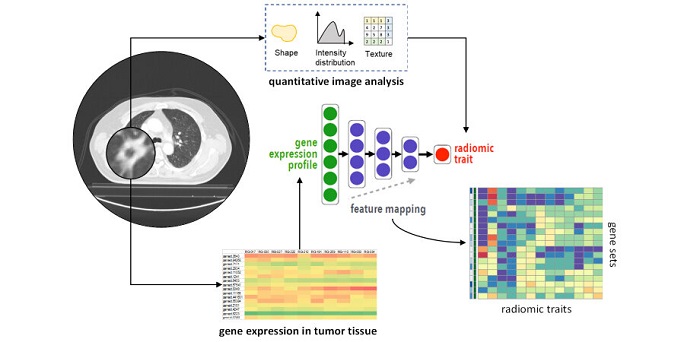
There are, however, several intricacies involved. The correlation of molecular patterns, such as gene expression and mutation, with image features (e.g., how a tumor appears in a CT scan), is commonly referred to as “radiogenomics.” This field is limited by its frequent use of high-dimensional data, wherein the number of features exceeds that of observations. Radiogenomics is also plagued by several simplifying model assumptions and a lack of validation datasets. While machine learning techniques such as deep neural networks can alleviate this situation by providing accurate predictions of image features from gene expression patterns, there arises a new problem: We do not know what the model has learned.
The ability to interrogate the model is critical to understanding and validating the learned radiogenomic associations. Their lab works on problems related to data integration, machine learning, and imaging informatics. In an earlier study, they used a method of interpreting a neural network called “gene masking” to interrogate trained neural networks to understand learned associations between genes and imaging phenotypes. They demonstrated that the radiogenic associations discovered by their model were consistent with prior knowledge. However, they only used a single dataset for brain tumors in their previous study, which means the generalizability of their approach remained to be determined.
Against this backdrop, the researchers have carried out a study investigating whether deep neural networks can represent associations between gene expression, histology (microscopic features of biological tissues), and CT-derived image features. They found that the network could not only reproduce previously reported associations but also identify new ones.
The researchers used a dataset of 262 patients to train their neural networks to predict 101 features from a massive collection of 21,766 gene expressions. They then tested its predictive ability on an independent dataset of 89 patients, while pitting its ability against that of other models within the training dataset. Finally, they applied gene masking to determine the learned associations between subsets of genes and the type of lung cancer.
They found that the overall performance of neural networks at representing these datasets was better than the other models and generalizable to datasets from another population. Additionally, the results of gene masking suggested that the prediction of each imaging feature was related to a unique gene expression profile governed by biological processes.
The researchers are encouraged by their findings. “While radiogenomic associations have previously been shown to accurately risk stratify patients, we are excited by the prospect that our model can better identify and understand the significance of these associations. We hope this approach increases the radiologist’s confidence in assessing the type of lung cancer seen on a CT scan. This information would be highly beneficial in informing individualized treatment planning.