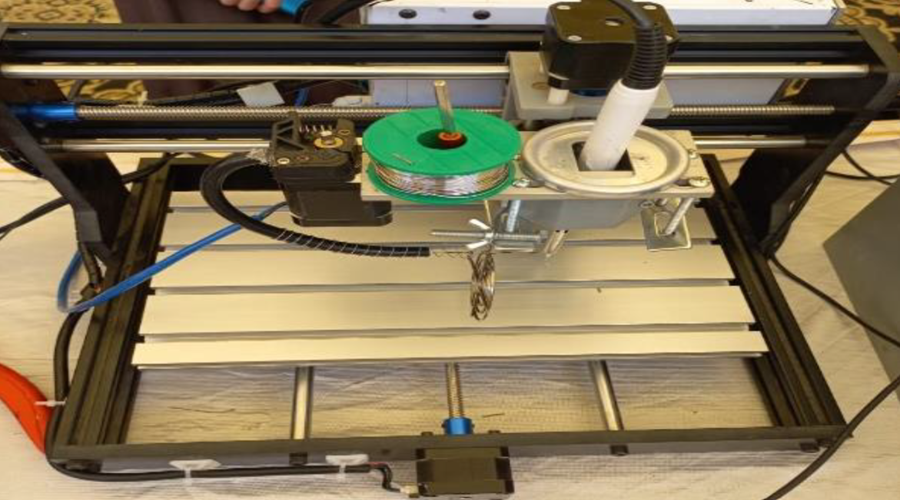
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) soldering is an automated process where soldering tasks are performed using a programmable CNC machine. It allows precise control over the soldering process, ideal for repetitive and intricate soldering tasks in electronic manufacturing. The CNC system guides the soldering tool along pre-defined paths to achieve accurate solder joints.
How CNC Soldering Works:
- Design Input: The process starts with CAD/CAM software to create a digital design of the soldering task.
- Programming: The design is converted into machine-readable G-code, which guides the CNC soldering machine.
- Machine Setup: The soldering tool (e.g., soldering iron, laser, or ultrasonic tool) is mounted on the CNC arm.
- Execution: The machine follows the programmed path, precisely applying solder to designated areas, ensuring consistent quality.
- Inspection: Automated or manual inspection ensures solder joints meet required standards.
CNC Soldering Process:
- Preparation:
- Load the components and PCB (Printed Circuit Board) onto the machine.
- Input the soldering design and settings.
- Heating and Solder Application:
- The CNC tool applies heat to the solder and component leads.
- Solder flows to form a secure joint.
- Cooling:
- The joint is allowed to cool naturally or with cooling systems to solidify.
- Quality Check:
- Joints are inspected for accuracy and integrity.
CNC Soldering Uses & Applications:
- Electronics Manufacturing: Ideal for PCBs in consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and medical devices.
- Prototype Development: Rapid soldering of prototype boards with consistent quality.
- Aerospace and Defense: Precise soldering for high-reliability applications.
- LED Assembly: Used for accurate placement and soldering of LED components.
- Telecommunications: Efficient soldering of intricate circuit boards for communication devices.
CNC Soldering Advantages:
- Precision: Ensures accurate soldering with minimal errors.
- Consistency: Delivers uniform quality across all joints.
- Speed: Automates repetitive tasks, reducing production time.
- Scalability: Suitable for both small-scale and mass production.
- Safety: Minimizes manual handling, reducing risks to operators.
- Versatility: Compatible with various soldering tools and techniques, including laser and ultrasonic soldering.
CNC Soldering Disadvantages:
- High Initial Cost: Significant investment in CNC machines and setup.
- Complex Setup: Requires skilled personnel for programming and maintenance.
- Limited Flexibility: Less adaptable to on-the-fly changes compared to manual soldering.
- Material Compatibility: May not suit all types of soldering materials or components.
- Maintenance Requirements: Machines need regular calibration and upkeep.
CNC soldering is a cornerstone of modern electronics manufacturing, combining efficiency and precision while offering cost-effective solutions for high-quality soldering needs.