Three-dimensional printing offers unique advantages, but still faces many challenges, for fabricating small, flexible robots that can navigate through the human body and other confined spaces, according to a review in the journal Science and Technology of Advanced Materials.
Researchers at South Korea’s Jeju National University examined the latest research and developments in fabricating soft robots using 3D printing technologies. Their study concludes that 3D printing is well suited to build robots that have complex external shapes together with an internally porous structure. Even so, the field is still new and major gaps must be addressed in order to print robots with multiple materials that readily adhere to each other.
Soft robots are made with highly compliant materials such as fluids, gels and polymers so they can mimic functions present in living organisms. In the last few years, there has been a significant trend toward using 3D printing for their manufacturing instead of conventional moulding and casting approaches.
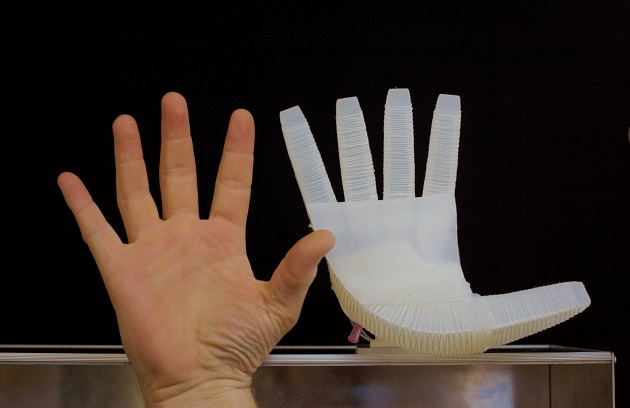
Many 3D printing technologies are available. They all convert digital data into three-dimensional objects by adding successive layers of a material until the object is fabricated. The printing technologies use different types of materials and approaches for layering them. For example, researchers used ‘selective laser sintering’ of powdered metals to develop a multi-finger soft robotic hand that can lift, grip, spin and precisely position objects.
Other materials used to 3D print soft robots include dielectric elastomers: polymers that change their size and shape when stimulated by an electric field; shape memory polymers, which change their shape in response to heat; and hydrogels that are affected by a variety of stimuli including heat, electricity, acidity, magnetism and light.
Soft robots are being tested for a variety of purposes inside and outside the human body. For example, a 3D printed soft silicone pump could be used as an artificial heart. 3D printed soft ‘micro-biobots’, which can travel through blood vessels or the gut, are being researched for monitoring diseases. Outside the body, soft robots are being developed for prosthetics, for monitoring vital signs, and for organ-on-a-chip devices that can replace animals in drug testing.
But many challenges remain to improve these technologies for clinical use. The materials sometimes shrink during the solidification process, for example. Also, 3D printing is yet too slow for mass production.
The commercial success of these technologies, the researchers conclude, will depend on developing rapid prototypes that can lead to mass-production. Robots must also be inexpensive and satisfy market needs.