Decision Tree Learning’s architecture is a tree-like, hierarchical structure employed in both classification and regression in supervised machine learning. It starts with a root node, which is the complete dataset and the starting point of the first split according to a chosen feature. From there, the tree splits into internal decision nodes, where each of them is a test on an attribute, and branches, which represent the results of those tests. The algorithm repeats recursively, splitting the data into subsets until reaching leaf nodes, where the terminal output is represented as either a class label or a numeric value.
Such an architecture is constructed based on algorithms such as CART (Classification and Regression Trees), which select the optimal splits based on evaluation of criteria such as Gini impurity or entropy. The aim is to produce a model imitating human decision-making by posing a series of questions that progressively give more particular conclusions. The ease of interpretability and simplicity of this organization make decision trees widely used in predictive analytics and data mining.
Types of Decision Tree Learning:
- Classification Tree
A Classification Tree is created to solve problems where the output variable is a category, i.e., it is a member of a particular class or category. The tree divides the data based on feature values that can best distinguish the categories. For each node, the algorithm selects the feature that gives the maximum information gain or decreases Gini impurity most. This goes on until the data has been separated into pure subsets, or leaf nodes, which are the final class prediction. For instance, it can distinguish between emails and non-spams.
- Regression Tree
A Regression Tree is employed when the target variable is continuous, i.e., it has numerical values. Rather than dividing data into categories, it estimates a numeric value by averaging the values in each leaf node. The tree splits data according to features that reduce the variance or mean squared error in the target variable. Each split is designed to produce subsets as homogeneous as possible based on the numerical output. For example: Predicting house prices, forecasting sales.
Decision Tree Learning Diagram:
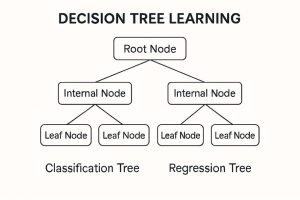
The figure shows the decision tree learning architecture, a supervised learning machine model that applies to both classification and regression learning. At the apex is the root node, which symbolizes the entire data set and makes the first decision based on a chosen feature. It divides into internal nodes, each symbolizing a point of decision which further divides the data along specific feature values. These internal nodes subsequently branch out to leaf nodes that give the terminal output either a class label for a classification tree or a numerical value for a regression tree. The left half of the diagram illustrates a classification tree where the decisions end up in discrete categories, and the right half illustrates a regression tree where the outputs are continuous values. The framework is binary and symmetrical, highlighting the way data recursively splits in order to make a predictive judgment. The graphical framework serves to demystify how decision trees work through the gradual elimination of possibilities based on feature divisions.
Conclusion:
Decision trees are not only model they’re reasoning frameworks. Their readability, interpretableness, and flexibility make them a starting point for data science, particularly when understanding and actionable results are paramount. From classifying emails to forecasting real estate values, decision trees provide a step-by-step, logical process to comprehend the data.








