As the world transitions towards Industry 5.0, the notion of smart factories is no science fiction. The concept of smart manufacturing revolves around collecting, analysing, and using data from multiple sources to automate and optimise processes. India’s Smart factory market is projected to grow at a 14.3% CAGR (2025-30) to reach USD 15.6 billion by 2026. Among the various industries, the electronics and semiconductors sector is expected to be the fastest-growing in the adoption of Industry 5.0. The concept of Industry 5.0 thrives on three basic pillars– human-centricity and collaboration, sustainability, and resilience.
The game of smart manufacturing is all about the usage of data. The one who has the most holistic variety of data is bound to excel in the adoption and implementation of smart factories. From advanced automation, using AI, harnessing updated IoT technology, and big data analytics, the real deal of manufacturing lies in how well data can be used. Apart from these, the biggest innovations in Industry 5.0 are the use of ‘cobots’, or as one would call them, collaborative robots. Among the various technological advancements, the ‘Human-Machine Interface’ (HMI) is projected to be the fastest-growing technology segment in the Indian Smart Factory market.
Shifting from Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 focused largely on technological advancement to boost the pace of production and its efficiency, and it was often said that this advancement of technology would eventually replace the human workforce. However, the trend changes with the adoption of Industry 5.0.
So, the idea now is that digitalisation will not make humans in industrial manufacturing obsolete; instead, it will integrate smart automation, systems, and devices in the workplace to promote cooperation and collaboration between humans and machines.
Technology in Smart Manufacturing
Core technologies under the smart manufacturing set-up of Industry 5.0 are said to work on edge-computing, cybersecurity measures, cloud-computing, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, and big data analytics.
Edge and cloud computing in Industry 5.0 smart manufacturing offer real-time responsiveness (Edge), enhanced human-cobot collaboration, greater flexibility for mass customization, improved security/privacy, reduced costs/bandwidth, and powerful predictive analytics, with the cloud handling heavy storage/complex AI while the edge provides speed and reliability for immediate action, enabling personalized, sustainable, and efficient production.
Man + Machine Middleware
The contemporary concept of smart factories is no longer just automation through machines. Today, it is all about the ‘coexistence’ of humans and machines, and that is exactly what everyone is focused on!

While there is a buzz about AI taking over human jobs in the coming future, the real deal is that humans are central to manufacturing; however, the role of the human workforce will shift from handling repetitive and laborious tasks to indulging in customisation and creativity.
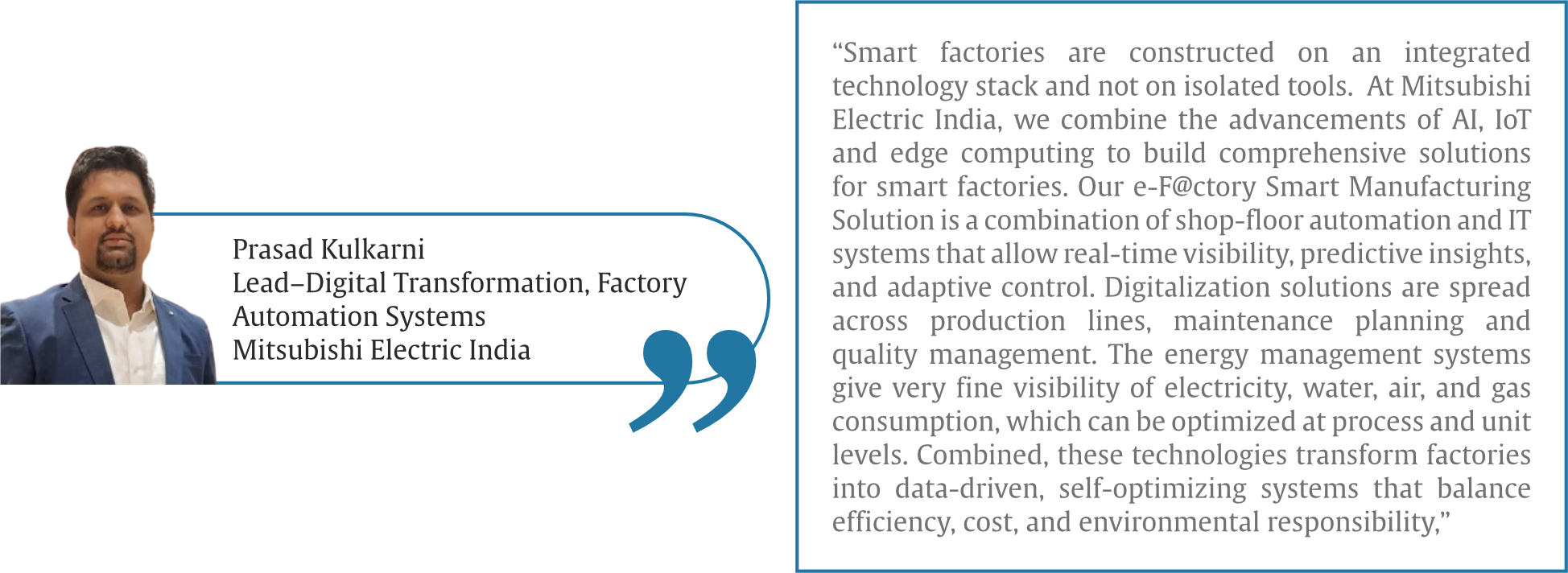
“The integration of AI and machine learning enables better human-machine collaboration where technology adapts to human needs on a real-time basis. IoT turns equipment into context-aware responsive assets. Digital twins enable engineers and operators to experiment in the virtual world, which is less risky and less cognitively demanding than the shop floor. Complex data is converted into easy-to-use visual and tactile interfaces with advanced HMIs, which can be used to make decisions faster and more safely,” reflects Prasad Kulkarni, Lead–Digital Transformation, Factory Automation Systems, Mitsubishi Electric India.
“Co” in Cobot
Imagine a workspace where a technician is hand-soldering a custom prototype while, just inches away, a robotic arm is flawlessly placing components the size of a grain of salt with 0.01mm precision. Meet your new favourite bench-mate. It doesn’t take coffee breaks, it never gets a “Monday morning” headache, and it can hold a PCB steady for hours without a single tremor. Cobots are the literal “Helping Hands” of Industry 5.0, filling the gap between rigid automation and the high-touch craftsmanship that modern electronics manufacturing requires.
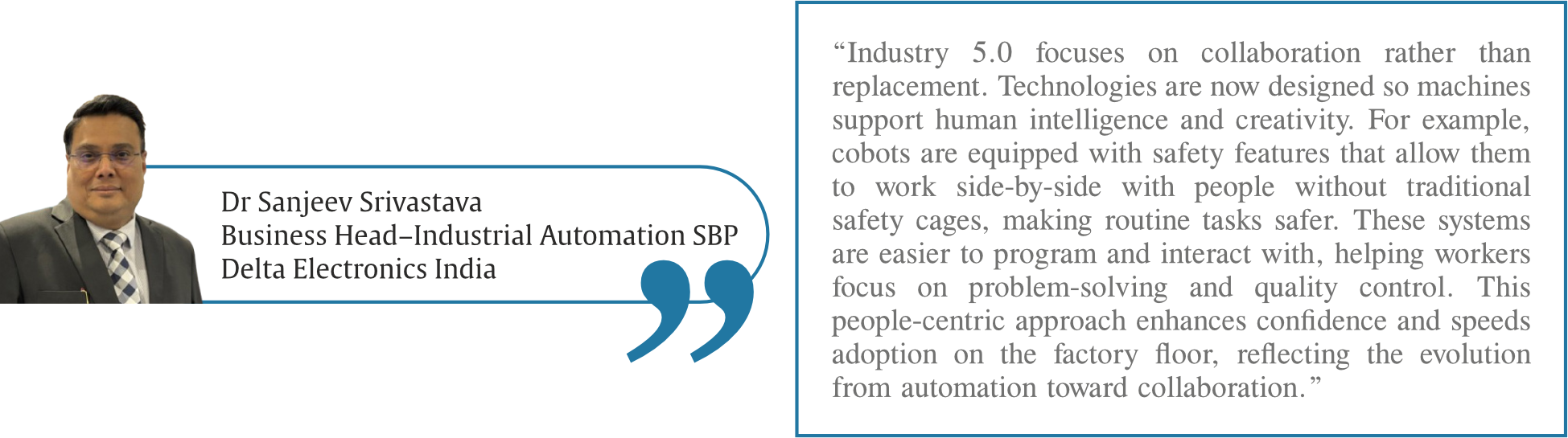
“Cobots are designed with safety and human collaboration in mind. They include sensors and control systems that detect human proximity and can instantly slow or stop motion to prevent accidents. Their flexibility and ease of programming make them suitable for varied tasks such as assembly, material handling, and packaging. These features help reduce worker fatigue and ergonomic risk while maintaining process consistency. When used properly, cobots enhance productivity and workplace safety, enabling humans to focus on tasks that require judgment and creativity,” underscores Dr Sanjeev Srivastava, Business Head–Industrial Automation SBP, Delta Electronics India.
Throwing light on the working mechanism of cobots, Prasad Kulkarni, Lead–Digital Transformation, Factory Automation Systems, Mitsubishi Electric India, detailed, “Cobots are designed with safety, flexibility, and ergonomics as core principles. They are specifically engineered to work safely alongside human operators. This is achieved through built-in safety mechanisms such as force and torque limitation, advanced vision systems, proximity sensing, and real-time feedback, which enable immediate response to human presence. From an efficiency standpoint, cobots deliver high consistency and precision in tasks such as calibration, complex assembly, inspection, sealant application, etc.”
Adoption and Challenges
The complete adoption of smart manufacturing under Industry 5.0 is still a work in progress, but “Adoption of Industry 5.0–aligned technologies is steadily increasing, particularly among organisations seeking flexibility, scalability, and workforce sustainability. While early adoption has been led by larger enterprises, interest from mid-sized manufacturers is also growing. In the long term, this trend will result in more resilient supply chains, faster response to market changes, and a workforce that is better supported by intelligent automation,” confirms Prateek Jain, COO and Co- founder of Addverb.
The International Federation of Robotics predicts that 35% of worldwide manufacturers will implement Industry 5.0 technologies (such as cobots) over the next decade to unite automated systems with human capabilities.
The shift is not expected to take too long; however, there are certain challenges that one may face in the course of time. “One challenge is integrating advanced automation with existing equipment and processes without overwhelming operators. Smart solutions must be powerful yet intuitive. Connectivity and cybersecurity are also critical as more systems communicate across networks. Additionally, helping the workforce upskill and get comfortable with new tools is essential. While intelligent automation can improve efficiency and safety, it requires thoughtful design and training support so technology feels empowering rather than disruptive in everyday operations,” explains Dr Sanjeev Srivastava, Business Head–Industrial Automation SBP, Delta Electronics India.
In Near Future
Industry 5.0 technologies are already in use across several industries, from automotive to electronics manufacturing. AI-based vision systems are supporting human-led quality inspection in the semiconductor and FMCG sectors for early detection of defects while allowing humans to take the final decisions. Simultaneously, “digital twins are widely used to simulate new production lines and train operators before commissioning, particularly in automotive and heavy industry, reducing ramp-up time and risk. At the same time, manufacturers in energy-intensive sectors such as automotive and metals are using data-driven energy optimisation to lower power consumption and emissions. Together, these examples show how factory automation is evolving to be more human-centric, sustainable, and resilient – not just more automated,” says Prasad Kulkarni, Lead–Digital Transformation, Factory Automation Systems, Mitsubishi Electric India.
Ultimately, Industry 5.0 marks a transition from “how fast can we build?” to “how well can we collaborate?” For the electronics B2B sector, this isn’t just a technical upgrade; it’s a cultural renaissance. By weaving the irreplaceable intuition of human craftsmanship into the tireless precision of smart manufacturing, we are moving beyond cold, rigid automation. The future of silicon and circuitry lies in this hybrid harmony where cobots and creators coexist to drive innovation that is as personal as it is powerful. In this new era, the most sophisticated component on the factory floor will always be the human touch.
By: Shreya Bansal, Sub-Editor







