When Quantum computers become more powerful and widespread, they will need a robust Quantum Internet to communicate. Purdue University engineers have addressed an issue barring the development of quantum networks that are big enough to reliably support more than a handful of users.
The method, demonstrated in a paper published in Optica, could help lay the groundwork for when a large number of quantum computers, quantum sensors, and other quantum technology are ready to go online and communicate with each other.
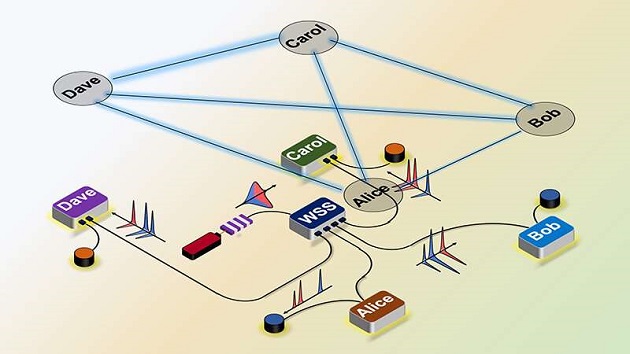
The team deployed a programmable switch to adjust how much data goes to each user by selecting and redirecting wavelengths of light carrying the different data channels, making it possible to increase the number of users without adding to photon loss as the network gets bigger.
If photons are lost, quantum information is lost—a problem that tends to happen the farther photons have to travel through fiber-optic networks.
“We show a way to do wavelength routing with just one piece of equipment—a wavelength-selective switch—to, in principle, build a network of 12 to 20 users, maybe even more,” said Andrew Weiner, Purdue’s Scifres Family Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering. “Previous approaches have required physically interchanging dozens of fixed optical filters tuned to individual wavelengths, which made the ability to adjust connections between users not practically viable and photon loss more likely.”
Instead of needing to add these filters each time that a new user joins the network, engineers could just program the wavelength-selective switch to direct data-carrying wavelengths over to each new user—reducing operational and maintenance costs as well as making a quantum internet more efficient.
The wavelength-selective switch also can be programmed to adjust bandwidth according to a user’s needs, which has not been possible with fixed optical filters. Some users may be using applications that require more bandwidth than others, similarly to how watching shows through a web-based streaming service uses more bandwidth than sending an email.
For a quantum internet, forming connections between users and adjusting bandwidth means distributing entanglement, the ability of photons to maintain a fixed quantum mechanical relationship with one another no matter how far apart they may be to connect users in a network. Entanglement plays a key role in quantum computing and quantum information processing.
“When people talk about a quantum internet, it’s this idea of generating entanglement remotely between two different stations, such as between quantum computers,” said Navin Lingaraju, a Purdue Ph.D. student in electrical and computer engineering. “Our method changes the rate at which entangled photons are shared between different users. These entangled photons might be used as a resource to entangle quantum computers or quantum sensors at the two different stations.”
Purdue researchers performed the study in collaboration with Joseph Lukens, a research scientist at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The wavelength-selective switch that the team deployed is based on similar technology used for adjusting bandwidth for today’s classical communication.
The switch also is capable of using a “flex grid,” like classical lightwave communications now uses, to partition bandwidth to users at a variety of wavelengths and locations rather than being restricted to a series of fixed wavelengths, each of which would have a fixed bandwidth or information-carrying capacity at fixed locations.
“For the first time, we are trying to take something sort of inspired by these classical communications concepts using comparable equipment to point out the potential advantages it has for quantum networks,” Weiner said. The team is working on building larger networks using the wavelength-selective switch.