In his most recent published research, appearing in Applied Thermal Engineering, City, University of London’s Dr. Martin White explores a novel organic Rankine cycle system, based on a two-phase expansion through numerical simulations of the system.
His paper, “Cycle and turbine optimization for an ORC operating with two-phase expansion,” considers the use of modern fluids whose properties could help to mitigate concerns around turbine damage, whilst allowing the benefits of two-phase expansion to be realized.
Waste heat from a range of industries, ranging from iron and steel to food and drink, is currently ejected into the environment. Thus, the recovery of this wasted energy could have a significant role in reducing the environmental footprint of the manufacturing sector and help to ensure future manufacturing practices are sustainable.
Dr. White, a lecturer in thermal power in the School of Mathematics, Computer Science and Engineering, says:
One of the most promising groups of waste-heat recovery technologies is those that are able to convert this waste heat into electricity. However, current technologies, typically based on the organic Rankine cycle (ORC) – which is similar to a steam cycle but operates with a different fluid rather than water—typically have relatively poor thermodynamic performance and are associated with high costs.
In a conventional ORC system, power is produced by the turbine which is designed to operate completely with a fluid that is in a gaseous state. This is done to avoid the presence of liquid droplets within the turbine that could damage or erode the machine. However, previous investigations have suggested that the admission of a two-phase fluid, which is a combination of liquid and vapor, could enhance the power output from these systems.
Dr. White believes that if a suitable turbine design intended for two-phase operation can be designed, the performance of ORC systems could be enhanced.
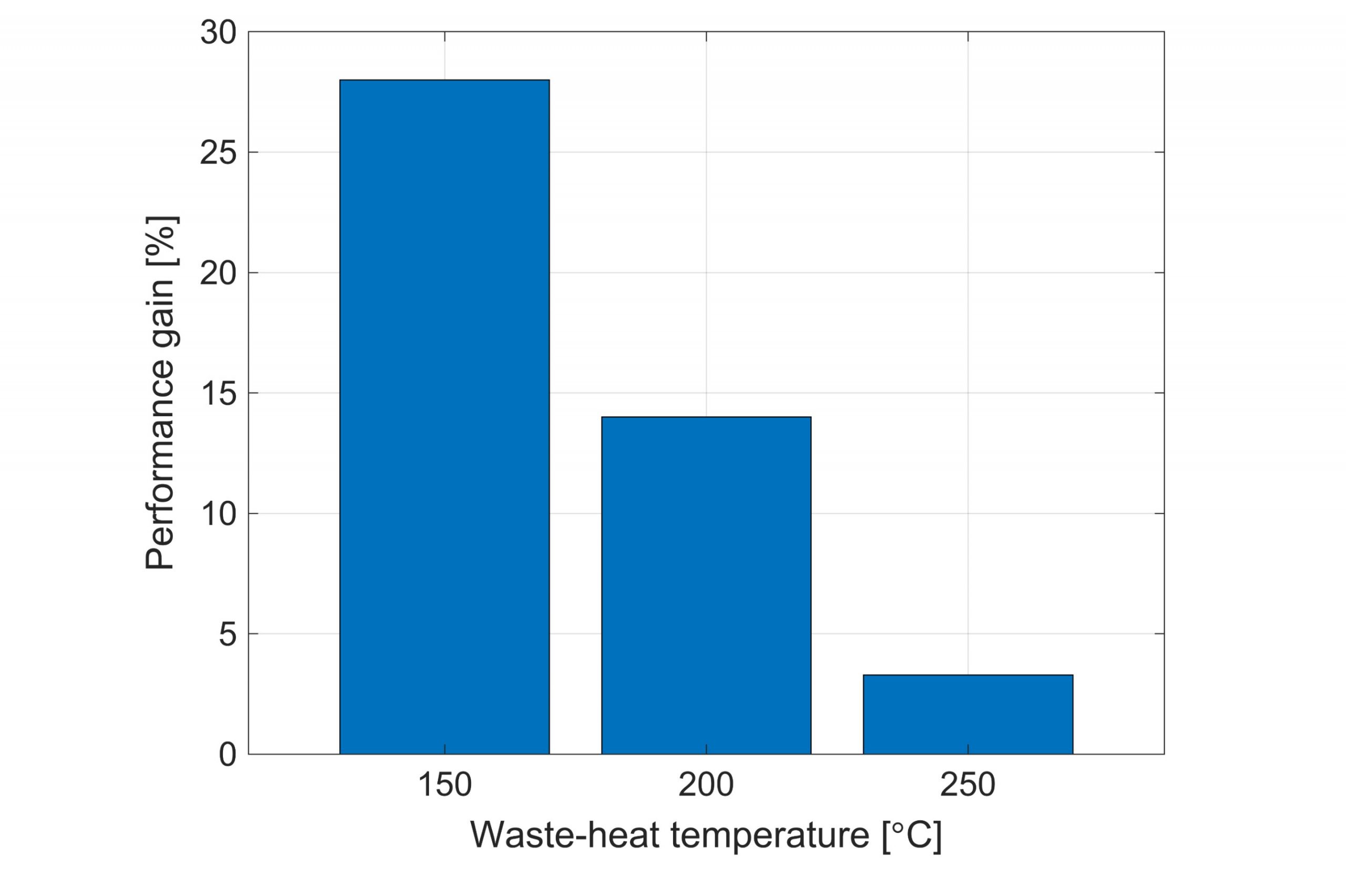
The simulations he has carried out indicate that for waste heat temperatures up to 250degrees centigrade, the introduction of two-phase expansion could generate up to 28% more power than conventional single-phase systems. Moreover, candidate designs for the turbine are proposed which require further investigation in later studies.