Courtesy: RoHM
AI’s unprecedented advancement is reshaping our world, but this transformation comes with the urgent challenge of sharply rising energy demands from data center infrastructure.
In response, Japan has launched an ambitious national strategy—the ‘Watt-Bit Initiative’—spearheaded by the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI). This comprehensive program aims to establish Japan as a global leader by developing ultra-efficient data centers strategically distributed across the nation. Through collaborative platforms like the ‘Watt-Bit Public-Private Council,’ METI is orchestrating a unified effort among key sectors—energy providers, telecommunications, data center operators, and semiconductor manufacturers—to turn this vision into reality.
Will AI Consume the World’s Electricity?
The explosive growth of generative AI technologies like ChatGPT has triggered an unprecedented surge in data center energy demands. Training and inference of complex AI models require enormous computational resources, supported by high-performance servers operating continuously around the clock.
This escalating demand for electricity not only places a significant strain on local environments but also raises concerns about the stability of the power supply. As AI continues to advance, the limitations of conventional power supply systems are becoming increasingly apparent.
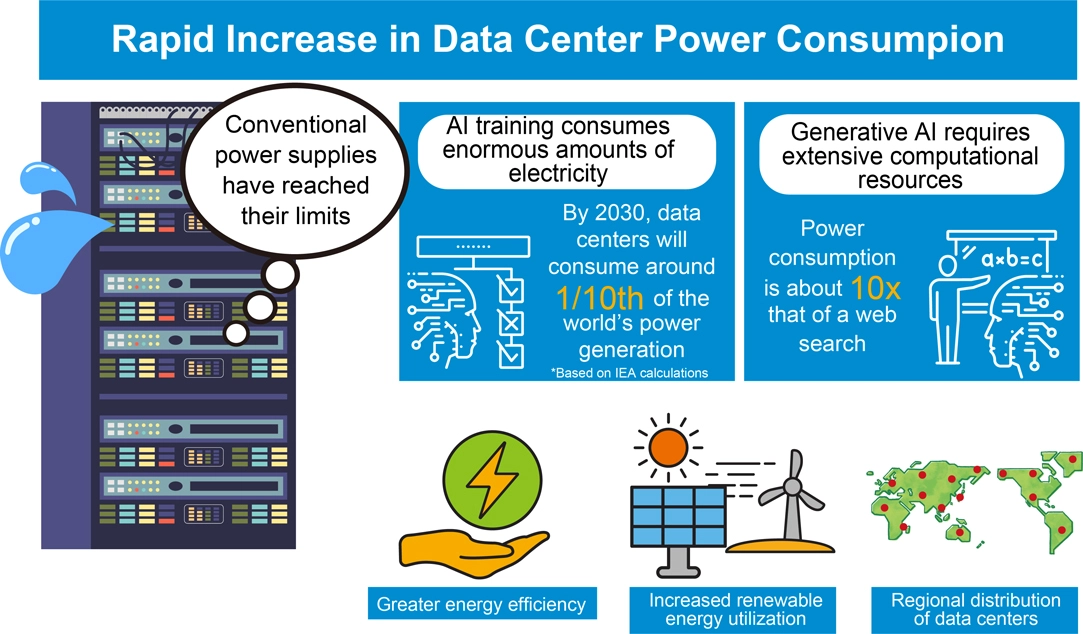
Against this backdrop, three urgent challenges emerge: improving energy efficiency, expanding the use of renewable energy, and optimizing the regional distribution of data centers. Achieving a sustainable society requires moving away from fossil fuel dependency and embracing renewable sources such as solar and wind power.
Utilizing Renewable Energy in Data Centers
Data centers, now an indispensable part of modern infrastructure, are at a major turning point.
Traditionally, urban data centers have been concentrated in metropolitan hubs like Tokyo to ensure low-latency communication for services requiring high-speed data access, including finance, healthcare, and edge computing. However, the surge in power consumption driven by AI adoption, coupled with the need for robust business continuity (BCP) in the face of large-scale natural disasters, is accelerating the shift toward decentralizing data centers into suburban areas.
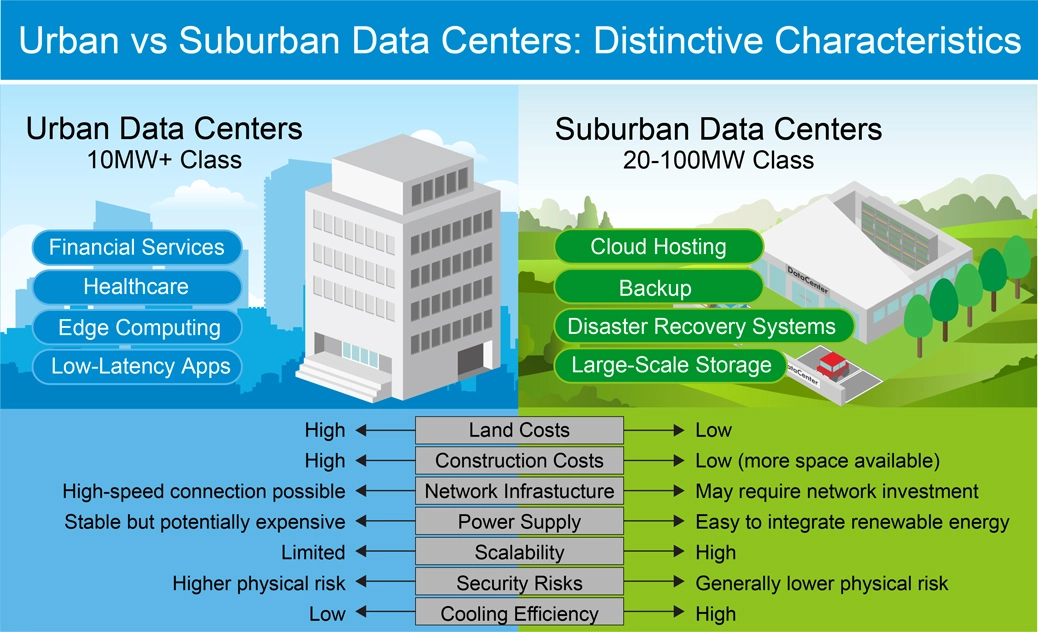
These new sites offer compelling advantages beyond just abundant available space. They enable seamless integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, benefit from surplus grid capacity for stable electricity, and leverage natural cooling from climate and water resources, dramatically reducing operational costs. As a result, suburban facilities are increasingly being adopted for modern workloads such as cloud hosting, backup, disaster recovery, and large-scale storage.
The Future of Server Rack Expansion
Urban data centers face severe land constraints, and even suburban data centers, where securing large plots is relatively easier, are approaching their limits in available space for server deployment.
To overcome this, server racks are evolving into high-density AI server racks designed to house a greater number of high-performance servers efficiently. Rather than expanding the total number of server racks, the industry is moving toward high-density configurations equipped with more CPUs, GPUs, and other functional boards, significantly boosting the computing power per rack to maximize performance within limited space.
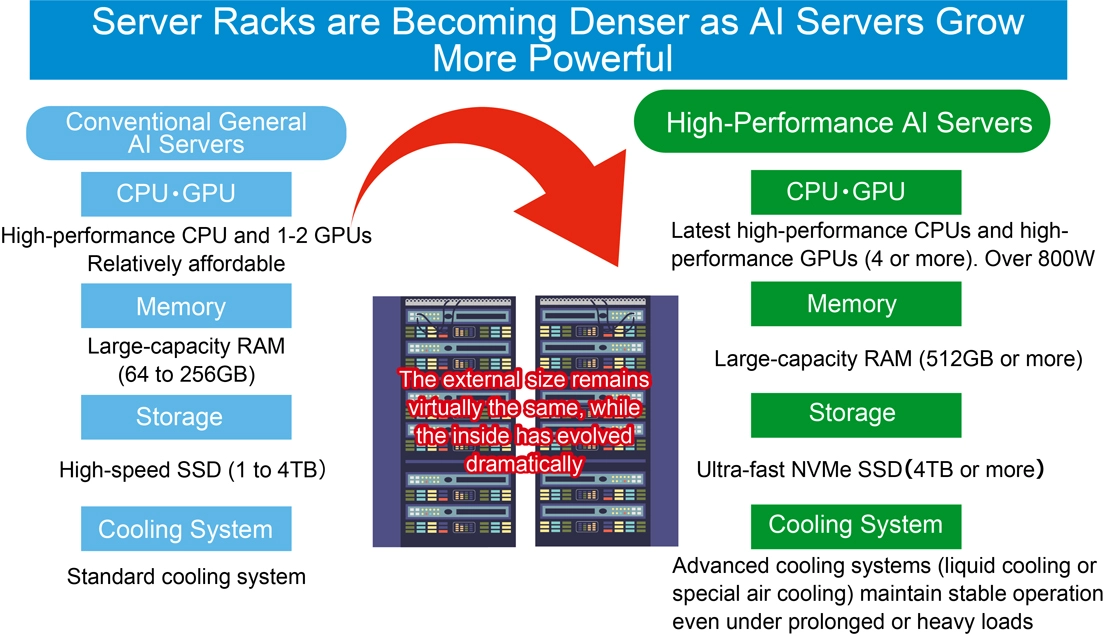
While the external appearance of server racks remains largely unchanged, their internal storage capacity has increased several fold.
This leap in performance and density demands a fundamental transformation of power delivery systems. Conventional multi-stage power conversion introduces significant energy losses, making efficient supply increasingly difficult. As a result, innovations such as reducing conversion stages and adopting high-voltage direct current (HVDC) architectures are gaining momentum, driving the need for SiC and GaN power semiconductors. ROHM, together with other industry leaders, is advancing technologies that support this transformation, enabling both higher performance and greater energy efficiency across entire data centers.
- Are Today’s Power Systems Sufficient?
The sharp rise in power consumption of high-performance AI servers—particularly GPUs—is forcing a fundamental redesign of existing data center power architectures. Conventional multi-stage power conversion incurs significant conversion losses, making efficient power delivery increasingly difficult.

In today’s data centers, high-voltage AC is supplied and gradually stepped down through multiple transformers and rectifiers before finally being converted into the low-voltage DC required by servers. Each stage of this process incurs losses, ultimately reducing overall efficiency. To address these challenges, data centers are expected to undergo key transformations aimed at enhancing both power conversion efficiency and reliability.
- Reducing Power Conversion Stages
A growing trend is the integration of multiple conversion processes—for example, converting high-voltage AC directly to DC, or stepping down high-voltage DC directly to the voltage used by servers. This approach significantly reduces the number of conversion steps, minimizing energy losses, enhancing overall system efficiency, and lowering the risk of failures.
- Supporting High-Voltage Input/High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Power Supplies
Server rack input voltages are shifting from traditional low-voltage 12VDC and 48VDC to higher levels such as 400VDC, and even 800VDC (or ±400VDC). Operating at higher voltages reduces transmission current, enabling lighter busbar designs.
At the same time, the adoption of HVDC systems is gaining momentum. Unlike conventional AC-based architectures, HVDC delivers DC power directly to server racks, reducing the need for multiple AC/DC conversion stages. This approach enhances energy efficiency, enables more flexible power management and bidirectional transmission, and simplifies integration with renewable energy sources.
- Increasing Adoption of SSTs (Solid State Transformers)
Transformer equipment is evolving from traditional designs to SSTs (Solid State Transformers) that leverage semiconductor technology. SSTs are expected to play a key role in significantly miniaturizing conventional equipment.
- Growing Demand for SiC/GaN Power Semiconductors
Building high-efficiency, high-voltage power systems requires performance levels that exceed the capabilities of conventional silicon (Si) semiconductors. This has made SiC and GaN power semiconductors indispensable. These advanced devices enable low-loss, high-frequency, high-temperature operation under high-voltage input conditions, greatly contributing to both the miniaturization and efficiency of power systems.

Moreover, as these technologies advance, their benefits extend beyond power systems to individual devices within server racks, further improving overall energy efficiency.
ROHM is accelerating the development of solutions for next-generation servers. In addition to existing products such as SiC/GaN/Si IGBTs, isolated gate drivers, cooling fan drivers, SSD PMICs, and HDD combo motor drivers from the EcoSiC, EcoGaN, and EcoMOS series, we are also developing high-current LV MOS, isolated DC-DC converters, DC-DC converters for SoCs/GPUs, and eFuses.
Power Semiconductors Driving Next-Generation AI Data Centers
- SiC Devices Ideal for High Voltage, Large Current Applications
SiC devices are particularly well-suited for sets requiring high voltages and currents. As server rack input voltages continue to rise, conventional 54V rack power systems face increasing challenges, including space limitations, high copper usage, and significant power conversion losses.
By integrating ROHM’s SiC MOSFETs into next-generation data center power systems, superior performance can be achieved in high-voltage, high-power environments. These devices reduce both switching and conduction losses, improving overall efficiency while ensuring the high reliability demanded by compact, high-density systems.
This not only minimizes energy loss but also reduces copper usage and simplifies power conversion across the entire data center.
- GaN Devices that Provide Greater Efficiency and Miniaturization
While SiC excels in high-voltage, high-current applications, GaN demonstrates outstanding performance in the 100V to 650V range, providing excellent breakdown strength, low on-resistance, and ultra-fast switching.
AI servers process far greater volumes of data than general-purpose servers, requiring high-performance GPUs, large memory capacity, and advanced software. This leads to higher power consumption, making efficient cooling and thermal management increasingly critical.
To address these challenges, GaN HEMTs – capable of high-speed switching (high-frequency operation) – are being integrated into power supply units to minimize power loss. This delivers major gains in power conversion efficiency, translating to substantial energy savings, lower operating costs, and reduced environmental footprint.
What’s more, GaN devices offer high current density, enabling a size reduction of approximately. 30-50% compared to conventional silicon devices. This not only improves space efficiency in power supplies and chargers, but also simplifies thermal design.
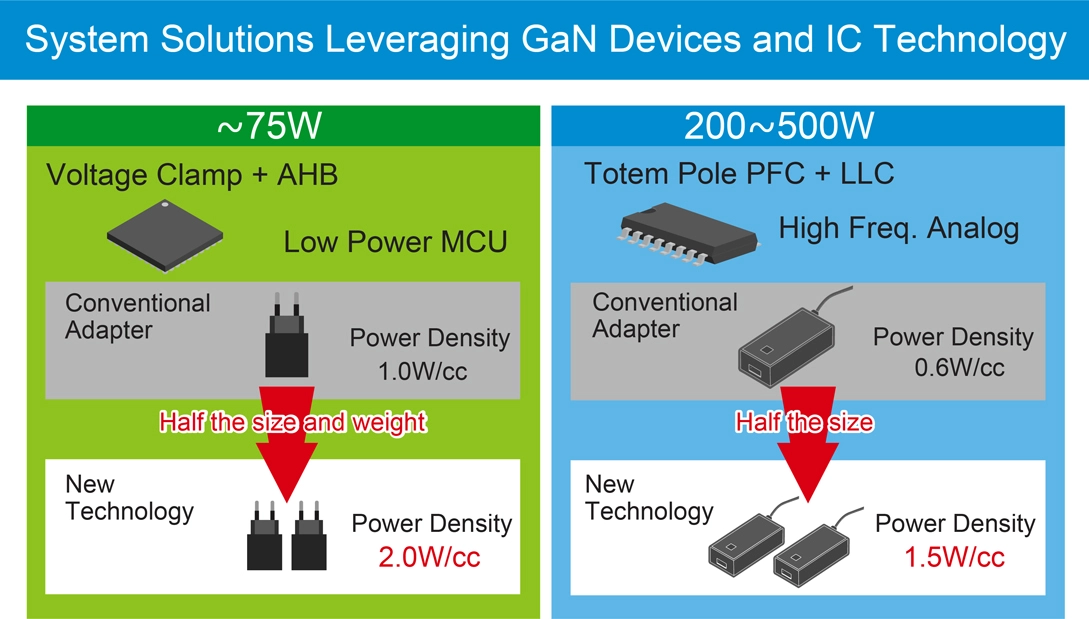
By reducing unit size and making effective use of freed-up space, the load on cooling systems can be alleviated, supporting overall system miniaturization and improved reliability. In addition, GaN’s high durability and suitability for high-frequency applications make it an ideal choice for data centers.
ROHM has succeeded in shortening the pulse width to as little as 2ns utilizing proprietary Nano Pulse Control technology, further enhancing the switching performance of GaN devices. Through the EcoGaN series, ROHM is expanding its lineup to meet the needs of AI data centers demanding compact, highly efficient power systems. The portfolio includes 150V and 650V GaN HEMTs, gate drivers, and integrated solutions that combine these components.
Conclusion
The evolution of AI, which shows no signs of slowing, comes with an inevitable surge in power demand.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global data center electricity consumption is expected to more than double in the next 5 years, reaching approximately 945 billion kWh. Around half of this demand is projected to be met by renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, signaling a major shift in how energy is generated and consumed in the power-hungry data center sector. Technologies like photovoltaics (PV) and energy storage systems (ESS) are gaining traction as essential components of this transformation.
ROHM is actively contributing to this transition with a broad portfolio of advanced power semiconductor technologies, including SiC and GaN devices. These solutions enable high-efficiency power systems tailored for next-generation AI data centers. ROHM is also accelerating the development of new products to meet evolving market needs, supporting a more sustainable and prosperous AI-driven future.







