In order to effectively navigate real-world environments, legged robots should be able to move swiftly and freely while maintaining their balance. This is particularly true for humanoid robots, robots with two legs and a human-like body structure.
Building robots that are stable on their legs while walking can be challenging. In fact, legged robots typically have unstable dynamics, due to their pendulum-like structure.
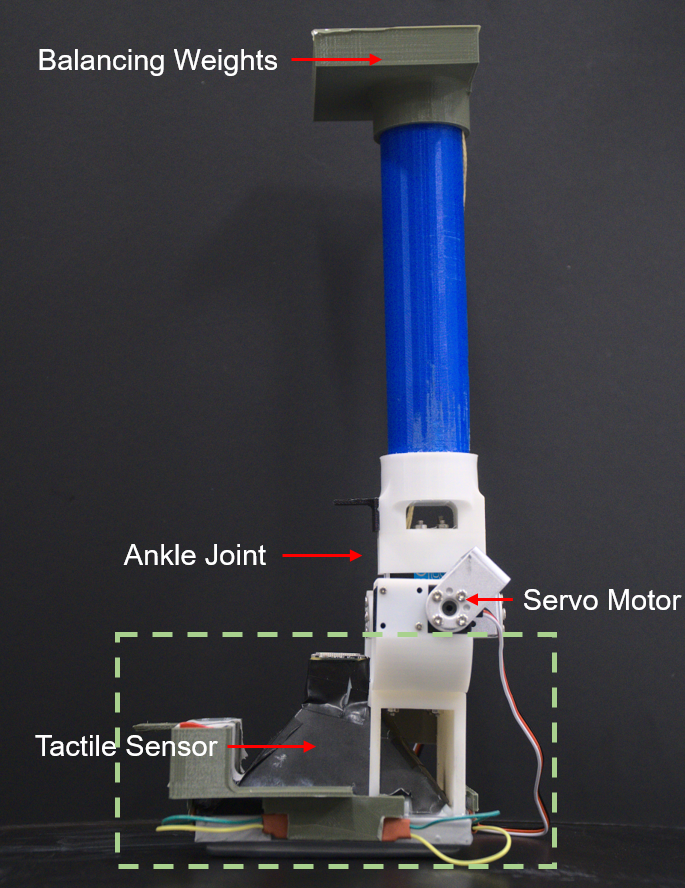
Researchers at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology recently developed a computer vision-based robotic foot with tactile sensing capabilities. When integrated at the end of a robot’s legs, the artificial foot can increase a robot’s balance and stability during locomotion.
Their recent paper focuses on the application of vision-based tactile sensing on legged robots. It is based on the idea that tactile/haptic sensing plays an important role in human interaction with the environment.
The overall objective of the recent study was to develop robots that can sense surfaces while completing tasks within a given environment, just as humans would. More specifically, they wanted to allow robots to balance their legs by sensing the ground beneath them. To achieve this, they inserted a soft, artificial “skin” under their robotic foot and installed a camera inside it, just above the “skin.”
“We deliberately painted special patterns on the inside of the skin, and the camera we used can capture this pattern,” researchers explained. “As the foot touches the ground, the soft skin will deform due to external forces. The pattern will also deform, and through the deformation of the pattern, we are able to obtain contact information such as the degree of the contact angle between the foot and the ground and tilting of the leg.”
The artificial foot developed by the researchers can collect far richer information about the surface a robot is walking on than conventional sensors. This information can then be used to improve a robot’s stability in scenarios where balancing systems based on traditional sensors might fail or perform poorly.
To convert images collected by the foot into contact-related data, the researchers used a new deep learning framework they developed. Subsequently, they carried out tests to evaluate the stability of a robotic leg with the foot integrated into it. They found that the foot could successfully estimate both the tilting angle of the surface beneath it and the foot’s pose.
In addition, the team carried out a series of experiments to test the overall feasibility and effectiveness of the tactile robotic system they created. Their system significantly outperformed conventional single-legged robotic systems, enabling greater balance and stability.
During the experiments, they found that the information contained in the contact phenomenon is more than we expected. We thus abandoned some redundant knowledge obtained by the sensor. However, high-level information, such as events (slip, collision, etc.) may also be detected or predicted by the tactile sensing foot.
In the future, the robotic foot created by this team of researchers could be used to develop legged robots that can maintain their stability when walking on different terrains and surfaces. In addition, it could enable more complex leg movements and locomotion styles in humanoid robots.
“In the future, we would like to apply our sensor on a real legged robot and conduct experiments related to robot-environment interaction,” researchers said. “We want to focus on how the tactile information is related to some events in locomotion, such as slip. And how to make use of this information in robot control.”