Soft robots driven by pressurized fluids could explore new frontiers and interact with delicate objects in ways that traditional rigid robots can’t. But building entirely soft robots remains a challenge because many of the components required to power these devices are, themselves, rigid.
Now, researchers from Harvard have developed electrically driven soft valves to control hydraulic soft actuators. These valves could be used in assistive and therapeutic devices, bio-inspired soft robots, soft grippers, surgical robots, and more.
Today’s rigid regulation systems considerably limit the adaptability and mobility of fluid-driven soft robots. Here, we have developed soft and lightweight valves to control soft hydraulic actuators that open up possibilities for soft onboard controls for future fluidic soft robots.
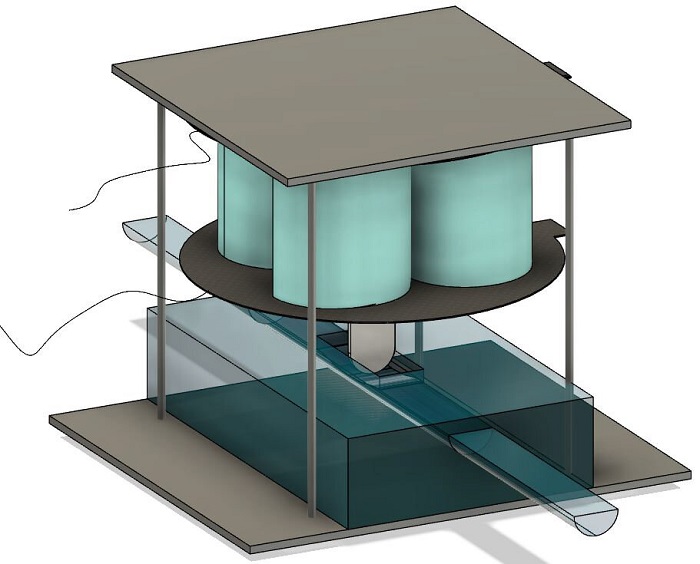
Soft valves aren’t new but so far none have achieved the pressure or flow rates required by many existing hydraulic actuators. To overcome those limitations, the team developed new electrically powered dynamic dielectric elastomer actuators (DEAs). These soft actuators have ultra-high power density, are lightweight, and can run for hundreds of thousands of cycles. The team combined these new dielectric elastomer actuators with a soft channel, resulting in a soft valve for fluidic control.
These soft valves have a fast response time and are able to control fluidic pressure and flow rates that match the needs of hydraulic actuators. These valves gave fast, powerful control of macro-and small-scale hydraulic actuators with internal volume ranging from hundreds of microliters to tens of millilitres.”
Using the DEA soft valves, the researchers demonstrated control of hydraulic actuators of different volumes and achieved independent control of multiple actuators powered by a single pressure source.
This compact and lightweight DEA valve are capable of unprecedented electrical control of hydraulic actuators, showing the potential for future onboard motion control of soft fluid-driven robots.