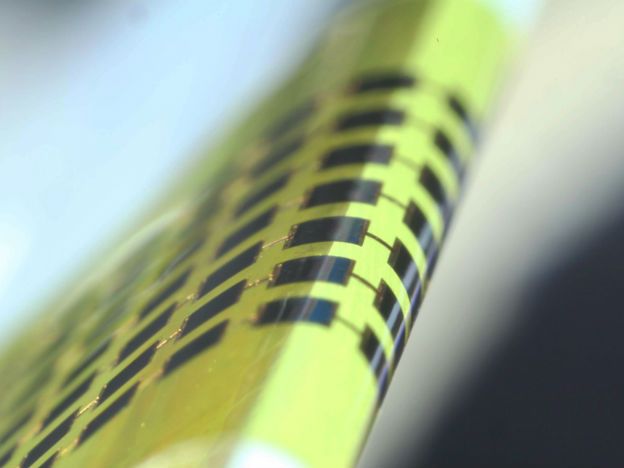
Scientists have developed new solar cells thinner than human hair and flexible enough to wrap around a pencil, that could power wearable electronics like fitness trackers and smart glasses.
The thin cells can be integrated onto frames of glasses or fabric and might power the next wave of wearable electronics, researchers said.”Our photovoltaic is about 1 micrometre thick,” said Jongho Lee, an engineer at the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology in South Korea.
One micrometre is much thinner than an average human hair. Standard photovoltaics are usually hundreds of times thicker, and even most other thin photovoltaics are 2 to 4 times thicker.The researchers made the ultra-thin solar cells from the semiconductor gallium arsenide. They stamped the cells directly onto a flexible substrate without using an adhesive that would add to the materials thickness.The cells were then “cold welded” to the electrode on the substrate by applying pressure at 170 degrees Celsius and melting a top layer of material called photoresist that acted as a temporary adhesive.The photoresist was later peeled away, leaving the direct metal to metal bond.The metal bottom layer also served as a reflector to direct stray photons back to the solar cells.
The researchers tested the efficiency of the device at converting sunlight to electricity and found that it was comparable to similar thicker photovoltaics.They performed bending tests and found the cells could wrap around a radius as small as 1.4 millimetres.The team also performed numerical analysis of the cells, finding that they experience one-fourth the amount of strain of similar cells that are 3.5 micrometres thick.”The thinner cells are less fragile under bending, but perform similarly or even slightly better,” Lee said. Other researchers have earlier reported solar cells with thicknesses of around 1 micrometre, but have produced the cells in different ways.The new method developed by Lee and his colleagues may be used to make very flexible photovoltaics with a smaller amount of materials.