High-performance, micro-sized electrochemical energy storage devices are essential for future miniaturized electronic devices, such as smart medical implants, wireless sensors, and the Internet of Things. Microbatteries (MBs) typically show higher energy density and more stable voltage output than micro-supercapacitors.
However, current MBs involve tedious construction procedures and unsatisfactory electrochemical performance. In addition, no methods exist to construct or manipulate a liquid microelectrode.
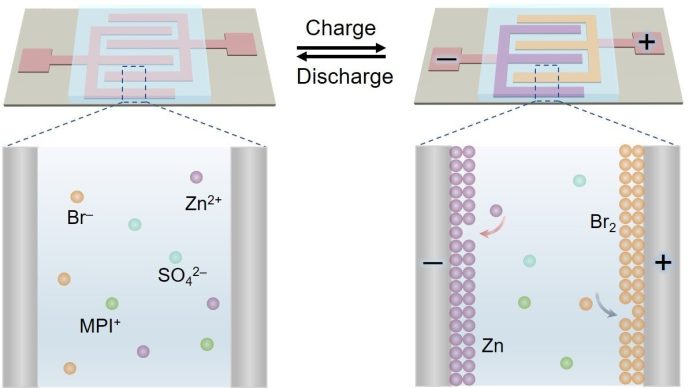
A joint research team led by Prof. Qu Liangti from Tsinghua University, Prof. Zhang Zhipan from the Beijing Institute of Technology, and Prof. Liu Feng from the Institute of Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMCAS) recently proposed a dual-plating strategy to rapidly construct new zinc–bromine microbatteries (Zn–Br2 MBs) with ultrahigh areal energy density and polarity-switchable functionality.
In this strategy, the in-situ plating of cathodes and anodes on microelectrodes takes place during the charging process, thus eliminating the synthesis of active materials. Furthermore, the troublesome and time-consuming mass matching of cathodes and anodes in previous methods can also be avoided, since the new method involves plating in cathode-anode pairs.
The researchers constructed the first aqueous Zn–Br2 MBs with liquid cathodes by using redox-active 1-methyl-3-propylimidazolium bromide, which not only prevents diffusion of Br3− but also shows fast kinetics during charging and discharging.
The Zn–Br2 MBs showed equal numbers of cathodes and anodes. They also delivered record-high areal capacity and energy density, more than 10 times that of most planar microbatteries.
Zn–Br2 MBs are polarity-switchable, thus allowing self-rectification during possible faulty operations such as wrongly connecting cathodes and anodes during charging.
“The combination between the suitable binding strength and loose network microstructures in electrodes endows Zn–Br2 MBs with outstanding performance,” said Prof. Liu.
This work offers new insights for promoting the development of miniaturized electronics through the fine design of their states, mechanical properties, and microstructures.