Courtesy: Analog Devices
In the digital age, reliable and high-speed wireless connectivity is no longer a luxury but a necessity. From bustling urban centers to remote rural areas, the demand for seamless communication is ever-increasing. This series will delve into the world of cellular distributed antenna systems (DAS) and how integrated solutions are revolutionizing wireless coverage. This first part of the series introduces the basics of cellular DAS, its importance, and the challenges it addresses.
Enhancing Connectivity in Challenging Environments
Definition of Cellular DAS: Modern commercial buildings are marvels of engineering, but they’re also notorious for blocking cellular signals. Materials like reinforced concrete, steel, and energy-efficient glass are excellent for sustainability and safety, but they act as RF shields, severely weakening or blocking mobile signals. A cellular DAS is a network of spatially separated antenna nodes connected to a common source through fiber optic cables, which provides wireless service within a geographic area or structure. It is designed to improve cellular coverage and capacity in areas where traditional macrocell solutions are insufficient. DAS systems are particularly useful in environments with high user density, such as large buildings, stadiums, and dense urban areas.
Importance of Cellular DAS: In today’s connected world with rising expectations for always-on mobile connectivity, poor cellular signal inside buildings is no longer acceptable. Reliable wireless coverage is crucial for both personal and business communications. Cellular DAS ensures that users can maintain high-quality connections, even in challenging environments. It is essential to maintain productivity, enhance user experience, and support critical applications such as emergency services and healthcare.
Challenges Addressed by Cellular DAS: Traditional macrocell solutions often struggle with indoor coverage, capacity limitations, and interference. These challenges can lead to dropped calls, poor data speeds, and unreliable connections. Cellular DAS addresses this challenge by extending and boosting signals inside buildings. A DAS is a network of antenna nodes distributed across a facility, all connected to a central source (often through a donor antenna and head-end equipment) to ensure even, reliable cellular coverage. These nodes amplify and redistribute the incoming signal to mobile users across multiple floors or large spaces. In short, cellular DAS overcomes these challenges by providing a robust, scalable, and flexible solution that can be tailored to specific needs. Figure 1 shows a typical fully DAS architecture.
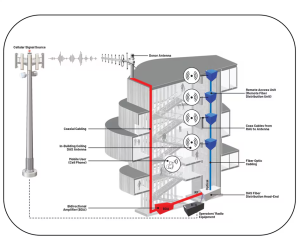
Figure 1: A Hybrid DAS Architecture
Key Components of Cellular DAS
The main components of a cellular DAS include:
- Head-End: The head-end is the central unit that connects to the base station and processes the signals. It is responsible for converting the signals from the base station into a format that the remote units can distribute.
- Transport Medium: The transport medium, such as fiber optic cables or coaxial cables, carries the signals from the head-end to the remote units. Fiber optic cables are preferred for their high bandwidth and low signal loss.
- Remote Units (Antennas): The remote units, or antennas, distribute the signals throughout the coverage area. They can be placed in strategic locations to ensure optimal coverage and capacity.
Benefits of Cellular DAS
Some of the key benefits of cellular DAS include:
- Improved Signal Strength: DAS systems can significantly improve signal strength–reducing the number of dropped calls and improving call quality.
- Enhanced Data Speeds: DAS systems can support higher data speeds by providing a more reliable and robust connection, which is essential for data-intensive applications.
- Better User Experience: Users benefit from a more consistent and reliable connection, which enhances their overall experience and satisfaction.
- Support for Multiple Carriers and Frequencies: DAS systems can support multiple carriers and frequency bands, making them highly versatile and future-proof.
Real-World Applications
Cellular DAS is widely used in various real-world applications, including:
- Large Buildings: In large office buildings, shopping malls, and other commercial spaces, DAS systems ensure reliable coverage and capacity for a large number of users.
- Stadiums and Arenas: DAS systems are essential for providing coverage to tens of thousands of spectators during events in large venues such as stadiums and arenas.
- Transportation Hubs: Airports, train stations, and other transportation hubs rely on DAS systems to ensure reliable communication for travelers and staff.
- Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals and other healthcare facilities use DAS systems to support critical communication and data transmission for patient care.
Conclusion
Understanding the fundamentals of cellular DAS is essential for grasping its significance in modern wireless networks. Cellular DAS plays a crucial role in ensuring reliable and high-speed connectivity by improving coverage and capacity. In the next part of this series, we will explore the different types of cellular DAS and their specific applications, providing a deeper understanding of how these systems can be tailored to meet various needs.







