Reinforcement Learning is a type of machine learning in which an agent learns to act by interacting with an environment, performing actions, and getting feedback in the form of reward or penalty. Rather than being instructed what to do, the agent finds out the optimum strategy by trial and error, trying to maximize cumulative rewards in the long run. It alternates between exploration of novel actions and exploitation of familiar good ones, adjusts according to changing circumstances, and frequently faces delayed rewards requiring long-term planning.
Reinforcement Learning Architecture is founded on a constant feedback cycle between an environment and an agent. The agent reads the state of the environment, selects an action based on its policy (its strategy for making decisions), and applies it. The environment reacts by changing to a different state and issuing a reward or penalty. As time progresses, the agent alters its policy based on this feedback to optimize long-term cumulative rewards. Key components are the policy (how to select actions), the value function (predicting future rewards), and possibly an environment model for planning.
Main types of Reinforcement Learning:
- Policy-Based Reinforcement Learning
Policy-based approaches bypass the value function and learn a policy directly, i.e., a mapping from states to actions. These approaches are especially beneficial for use in high-dimensional or continuous action spaces. They learn the policy with methods such as gradient ascent. REINFORCE and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) are examples of popular algorithms used in this category, providing stability and training efficiency.
- Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
Model-based methods consist of creating an environment model that estimates the next state and reward based on a current state and action. The agent utilizes this model to reason about future consequences and decide its actions. This approach is potentially more sample-efficient than model-free methods. Some examples are Dyna-Q, which combines planning and learning, and Monte Carlo Tree Search, applied in game-playing agents.
- Actor-Critic Methods
Actor-Critic methods combine the advantages of value-based and policy-based approaches. The actor selects what action to perform, and the critic judges how well the action was chosen through a value function. Double structure diminishes variance and enhances learning stability. A3C (Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic) and DDPG (Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient) algorithms are most commonly applied in continuous control problems.
Reinforcement Learning Architecture:
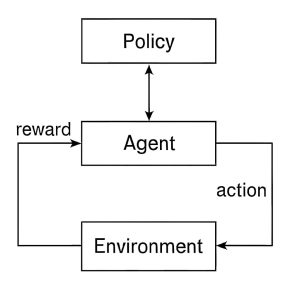
The diagram depicts the basic structure of a reinforcement learning system, showing how an agent learns to behave optimally by interacting with its environment. At the top, the policy determines the agent’s choices by mapping states to actions. The agent, shown centrally, applies this policy to choose an action that it then performs in the environment. The environment responds with a reward given in feedback form, which is an indication of the success of the performed action. This reward is fed back to the agent so it can modify its policy and make better decisions in the future. The policy of cyclical flow from agent to agent, agent to environment through action, and environment to agent through reward perfectly describes trial-and-error learning characteristic of reinforcement learning. Gradually, this cycle enables the agent to improve its plan and achieve maximum cumulative rewards through ongoing interaction and learning.








